| Click to view larger image |
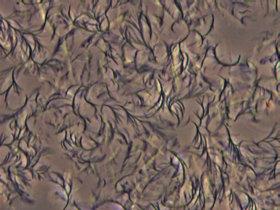
Mannitol dioctanoate in canola oil self assembles into a crystalline network that encapsulates the oil, causing it to take on a semisolid form.
Mannitol and sorbitol dioctanoates could provide alternatives to trans fats linked to obesity, coronary artery disease and diabetes
Researchers at The City College of New York have reported the successful transformation of vegetable oils to a semisolid form using low-calorie sugars as a structuring agent. The findings portend the development of alternatives to structured oil products produced using saturated/trans fatty acids, which have been linked to coronary artery disease, obesity and diabetes.
The team, led by City College Professor of Chemistry George John, tested two sugar alcohol-based gelators, mannitol dioctanoate (M8) and sorbitol dioctanoate (S8), as structuring agents for four refined vegetable oils purchased at local grocery stores: canola oil, olive oil, soybean oil and grape seed oil. Both are amphiphiles – i.e. molecules that are attracted to water and fats – consisting of two octanoic acid chains (C8) appended to a sugar alcohol molecule.
Oils are transformed to semisolid forms known as structured oils. The best known of these are vegetable oil and margarine. Structured oils are also contained in candy and cake frosting.
“We have demonstrated the first sugar-based thickening agents for oil,” said Professor John, whose previous investigations into the use of amphiphiles to solidify oil in the presence of water demonstrated their potential use in oil spill cleanups. He added that the two agents meet both Food & Drug Administration and GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) safety specifications, so they can be used for food processing.
Both M8 and S8 demonstrated excellent gelation tendencies for all of the oils that were tested, and the gels remained stable for several months. When mixed with the oils, the gelation agents self-assembled into three-dimensional crystalline networks that encapsulated the oils in liquid stage. Optimal gelation was achieved at structuring agent concentrations between three percent and five percent.
However, some differences between the two agents were reported. For example, mannitol gels were opaque in appearance while those made with sorbitol were translucent. That was because M8 yields a more densely packed network while the network of S8 gels consisted of needle-like microcrystallites.
Mannitol was found to be a more efficient gelator, producing stronger gels. However, Professor John pointed out that sorbitol-based gels, which have finer structures and appear more translucent, would be better suited for specific applications. “The multi-functionality and tunability of sugar-based gelators presents opportunities to develop next-generation oil thickeners,” he added.
The findings were reported in the November 15 issue of the Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry (J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, DOI: 10.1021/jf401987a). In addition to Professor John, the team consisted of Swapnil R. Jadhav and Hyeondo Hwang from City College and Qingrong Huang from Rutgers University.
About The City College of New York
Since 1847, The City College of New York has provided low-cost, high-quality education for New Yorkers in a wide variety of disciplines. More than 16,000 students pursue undergraduate and graduate degrees in: the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences; the Bernard and Anne Spitzer School of Architecture; the School of Education; the Grove School of Engineering; the Sophie Davis School of Biomedical Education, and the Colin Powell School for Civic and Global Leadership. U.S. News, Princeton Review and Forbes all rank City College among the best colleges and universities in the United States.
MEDIA CONTACT
Ellis Simon
p: 212.650.6460
e:
esimon@ccny.cuny.edu