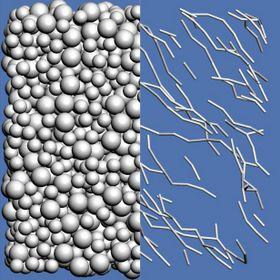
Sheared suspension of spheres occupying 52 percent of a volume, alongside images of "force chains;" i.e., the paths connecting spheres as they come into contact with their neighbors. The top image shows the spheres sheared before the transition to discontinuous sheared thickened.
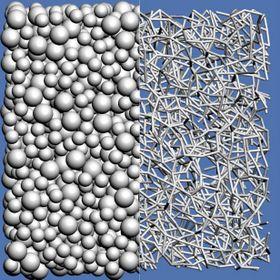
An increase in the rate of shearing of just 50 percent puts the suspension above the transition to DST, as depicted by the dense network of connections.
Levich Institute simulation of discontinuous shear thickening could lead to improved processing of materials in suspension
A new model by a team of researchers with The City College of New York’s Benjamin Levich Institute may shed new understanding on the phenomenon known as discontinuous shear thickening (DST), in which the resistance to stirring takes a sudden jump. Easily observed in a ‘kitchen experiment’ by mixing together equal amounts of cornstarch and water, DST occurs because concentrated suspensions of hard particles in a liquid respond differently than normal fluids to shear forces.
Because many materials are handled in industrial applications as suspensions, engineers need to understand how to predict their flow properties. However, they have been hard-pressed to understand DST and calculate when it will occur during processing. Since concentrated suspensions are found in everything from consumer products to cement, a range of industries stand to find better ways to manage suspensions.
For simple liquids, such as water or glycerin, resistance increases in proportion to the stirring speed. However, in complex fluids such as suspensions, emulsions and polymers the relationship is not proportional. Resistance increases either faster than the stirring speed – shear thickening – or slower – shear thinning. DST occurs when resistance increases suddenly.
Research associates Ryohei Seto and Romain Mari and chemical engineering Professors Jeffrey Morris and Morton Denn set out to develop a model that would predict how resistance changes in relation to stirring speed. Their findings were reported in “Physical Review Letters” in November.
The model modifies the classical fluid mechanics approach to suspension behavior, in which liquid lubrication keeps particles from contact, to permit contact and to include forces resulting from friction as particles move past one another.
As friction increases two or more particles can act like a single entity with regard to the surrounding fluid. When concentrations of particles and the shear rate reach sufficient levels, the particles form temporary chains that can fill space. This causes jamming, which can make flow difficult or even impossible.
Using the model, the team was “able to accurately reproduce experimental observations of the steep viscosity versus shear rate curves and their evolution with packing friction, both of which are first for numerical simulations,” Dr. Eric Brown, Yale University assistant professor of mechanical engineering and materials science, wrote in a commentary published in “Physics.”
Future investigations will address moving beyond a simulation “that follows the mechanics of a finite number of particles in a cube to predicting the flow of concentrated suspensions in arbitrary geometries,” Professor Denn noted. “A long-term goal is to be able to develop a ‘continuum’ description of concentrated suspensions in which the behavior is averaged over large numbers of particles.”
On the Internet
About The City College of New York
Since 1847, The City College of New York has provided low-cost, high-quality education for New Yorkers in a wide variety of disciplines. More than 16,000 students pursue undergraduate and graduate degrees in: the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences; the Bernard and Anne Spitzer School of Architecture; the School of Education; the Grove School of Engineering; the Sophie Davis School of Biomedical Education, and the Colin Powell School for Civic and Global Leadership. U.S. News, Princeton Review and Forbes all rank City College among the best colleges and universities in the United States.
MEDIA CONTACT
Ellis Simon
p: 212.650.6460
e:
%65simo%6e@ccny.cuny
.e%64u" rel="nofollow">
esimon@ccny.cuny.edu